이 포스팅에서는 Doubly linked list의 특징을 알아보고
파이썬으로 Doubly linked list의 삽입, 삭제, 조회를 구현해보도록 하겠습니다.
# Doubly linked list 란?
Doubly linked list는 각 노드에 자료 공간과 두 개의 포인터 공간이 있고, 각 노드의 포인터는 이전 노드와 다음 노드를 가리킵니다.
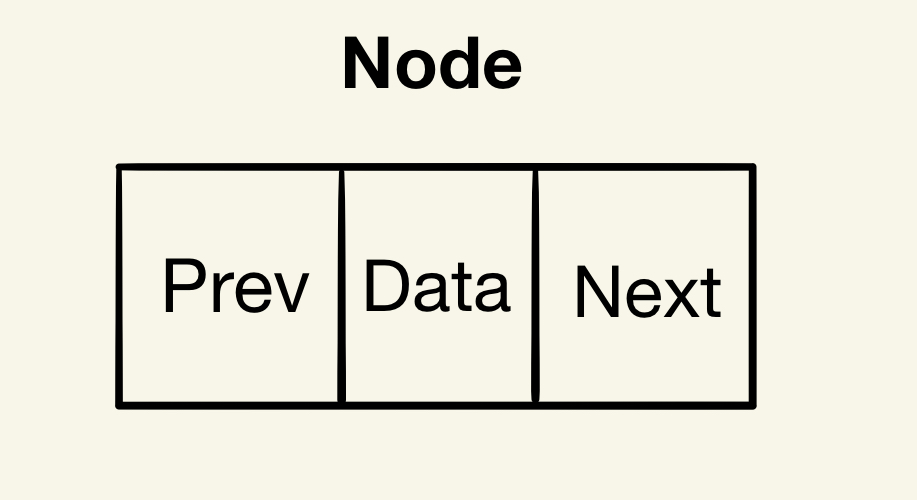
# 이중 연결 리스트의 특징, 장점, 단점은요
단순 연결리스트와 이중 연결 리스트의 차이는 prev를 가리키는 포인터 공간이 추가되면서 이전 노드에 대한 정보를 알 수 있다는 점입니다. 이로인해 단순 연결 리스트로는 할 수 없는 역으로 출력하는 것이 가능하고, 특정 노드의 이전 노드를 삭제하거나 특정 노드의 이전에 삽입하는게 가능해졌습니다. 그러나 단순 연결 리스트 자료구조 만으로도 기능이 충분하다면 포인터 공간을 추가하여 메모리 공간을 낭비하지 않는게 좋습니다.
# Doubly linked list 구현하기
# 삽입
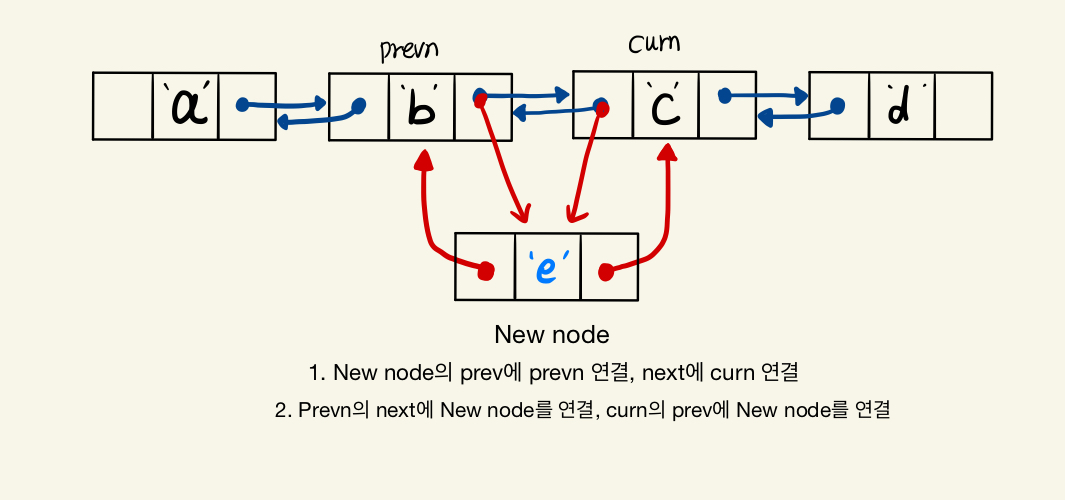
# 삭제

# 파이썬 코드
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
|
# Node
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, data):
self.prev = None
self.data = data
self.next = None
class DoublyLinked_list(object):
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def append(self, node):
if self.head:
curn = self.head
while curn.next:
curn = curn.next
curn.next = node
node.prev = curn
else:
self.head = node
def insertNodeAtIndex(self, idx, node):
prevn = None
nextn = None
# 맨 앞에 추가
if idx == 0:
if self.head:
nextn = self.head
self.head = node
self.head.next = nextn
nextn.prev = self.head
else:
self.head = node
# 중간과 맨 끝에 추가
else:
cur_i = 0
curn = self.head
while cur_i < idx:
if curn:
prevn = curn
curn = curn.next
else:
break
cur_i += 1
if cur_i == idx:
node.prev = prevn
node.next = curn
prevn.next = node
if curn:
curn.prev = node
else:
print(-1)
return -1
def getDataIndex(self, data):
curn = self.head
cur_i = 0
while curn:
if curn.data == data:
return cur_i
curn = curn.next
cur_i += 1
print(-1)
return -1
def insertNodeAtData(self, data, node):
index = self.getDataIndex(data)
if index >= 0:
self.insertNodeAtIndex(index, node)
else:
# print(-1)
return -1
def deleteAtIndex(self, idx):
nextn = None
prevn = None
cur_i = 0
if idx == 0:
if self.head:
self.head = self.head.next
self.head.prev = None
return
else:
print(-1)
return -1
curn = self.head
while cur_i < idx:
if curn.next:
prevn = curn
curn = curn.next
nextn = curn.next
else:
break
cur_i += 1
if cur_i == idx:
if nextn:
nextn.prev = prevn
prevn.next = nextn
else:
print(-1)
return -1
def print(self):
curn = self.head
string = ''
prevn = None
while curn:
string += str(curn.data)
if curn.next and curn.prev == prevn:
string += '<->'
prevn = curn
curn = curn.next
print(string)
if __name__ == "__main__":
dl = DoublyLinked_list()
dl.append(Node(1))
dl.append(Node(2))
dl.append(Node(3))
dl.append(Node(4))
dl.append(Node(6))
dl.print()
dl.insertNodeAtIndex(5,Node(7))
dl.print()
dl.insertNodeAtData(6, Node(5))
dl.print()
dl.deleteAtIndex(6)
dl.print()
|
cs |
'Data structure' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Python으로 구현하는 자료구조 : Heap (1) | 2019.05.11 |
|---|---|
| Python으로 구현하는 자료구조 : Linked List (3) Circular linked list (0) | 2019.05.10 |
| Python으로 구현하는 자료구조 : Linked List (1) Singly linked list (0) | 2019.03.31 |
| Python으로 구현하는 자료구조 : Stack (0) | 2019.03.31 |
